- Home
- About us
- Products
- Deep Groove Ball Bearing
- Ball Screw
- Self-aligning Ball Bearing
- Spherical Roller Bearing
- Thrust Aligning Roller Bearing
- Tapered Roller Bearing
- Thrust Ball Bearing
- Angular Contact Ball Bearing
- Thrust Roller Bearing
- Cylindrical Roller Bearing
- Pillow Block Bearing
- Machinery Equipment
- Thrust Conical Roller Bearing
- Bearing Cage
- Discount and Promotion all bearing
- Steel Balls
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
How to Choose Bearing Tolerance to Ensure The Motor Bearing System Operation
time2020/11/11
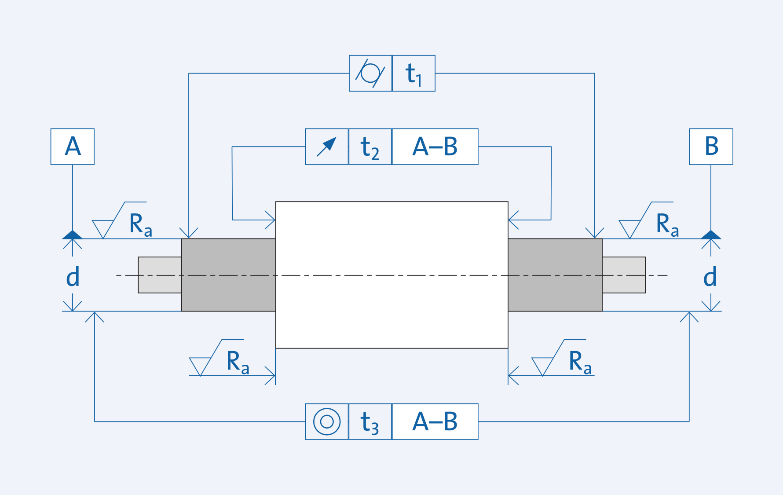
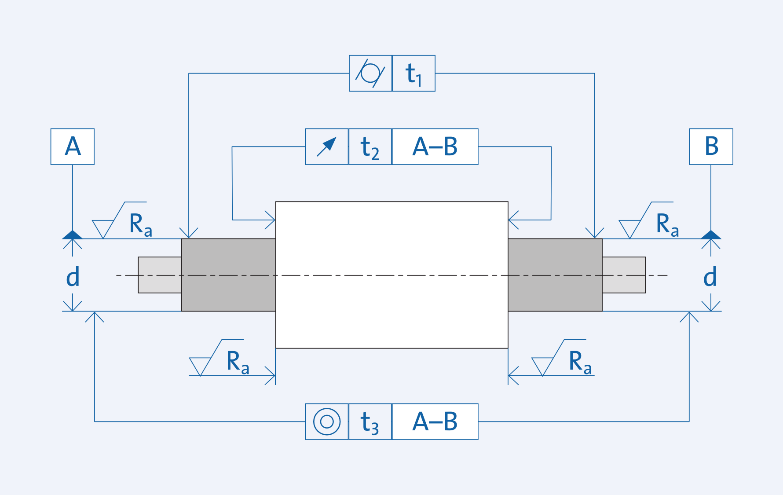
- Bearing tolerance refers to the accuracy of determining the size, that is, the allowable variation range of the size. Choose right tolerance is important.
How to Choose Bearing Tolerance to Ensure The Motor Bearing System Operation
Condition classification of bearing rotation
The bearing rotation condition refers to the bearing ring relative to the load, such as rotating load, static load, and variable load. Rotating load refers to when the bearing ring is rotating and the load is in a certain direction. Or the bearing ring is stationary and the load is rotating. In the process of one revolution of the bearing ring, all points on the raceway bear the load. Under the rotating load, the bearing ring with clearance fit may rotate between its mating surface and cause wear of the contact surface. That is the running ring problem of the bearing. Therefore, the bearing ring subjected to rotating load must adopt an interference fit.
When the bearing ring is stationary and the load has a fixed direction, or the bearing ring and the load rotates at the same speed, then the load always acts on the same position on the raceway. This situation is called a static load. In this case, the bearing ring generally does not rotate between its mating surface. Therefore, unless there are other reasons, the bearing ring does not need an interference fit.
Unfixed load refers to the load caused by some changing external forces, shock loads, and vibration and imbalance in high-speed machinery. In this case, the direction of the load will also change, so you can not have an accurate judgment. When you can't determine the load direction, especially when the load is heavy, it is best to use an interference fit for both bearing rings. But if the outer ring needs to be able to move freely in the axial direction of the bearing housing, under working conditions where the load is not too large, a slightly looser tolerance fit than the rotating load.
Bearing load and bearing tolerance selection
As the load increases, the bearing may deform, so the inner ring of the interference fit may also become loose. The rotating load affects the bearing and causes the inner ring to creep. So the amount of interference depends on the size of the load. The greater the load, especially when there is an impact load, the greater the amount of interference required.
Matching relationship of the bearing inner ring
For different rotation and load conditions, the matching relationship of the bearing inner ring is different:
(1) Tolerance selection under constant load you should select according to the relationship between the interference of the rotating ring and the clearance fit of the static ring.
●The inner ring rotates, the outer ring is stationary, and the load is constant radial. At this time, the inner ring bears a rotating load, and the outer ring is a static load. For example, motor bearings driven by belt pulleys belong to this type. You should use an interference fit for the inner ring and a small clearance fit for the outer ring.
●The inner ring is stationary, the outer ring is rotating, and the load is constant radial. For example, automobile hub bearings are of this type. The inner ring of the bearing bears a static load, and the outer ring is a rotating load. You should use an interference fit for the outer ring and a clearance fit for the inner ring.
(2) When the load rotates with the bearing ring, you should select the tolerance according to the relationship between the rotating ring clearance and the interference fit of the stationary ring.
●The inner ring rotates, the outer ring is stationary, and the load rotates with the inner ring. Such as vibrating machinery and vibrating screen, the inner ring bears a static load, and the outer ring is a rotating load. You should use an interference fit for the outer ring and a clearance fit for the inner ring.
●The inner ring is stationary, the outer ring rotates, and the load rotates with the outer ring. Such as a rotary crusher, the inner ring is a rotating load, and the inner ring is a static load. You should use an interference fit for the inner ring and a clearance fit for the outer ring.
